Ethereum Foundation researcher Dankrad Feist introduced Ethereum EIP-9698, a proposal aiming to scale the network by increasing the Ethereum gas limit by 100 times over four years. If implemented, Ethereum EIP-9698 could potentially raise Ethereum’s capacity to 2,000 transactions per second (TPS).
Currently, Ethereum processes around 14–20 TPS based on a 36 million gas limit, according to YCharts. The network’s theoretical maximum stands near 119 TPS. In comparison, Solana processes 800 to over 1,000 TPS, with a theoretical capacity of 65,000 TPS.
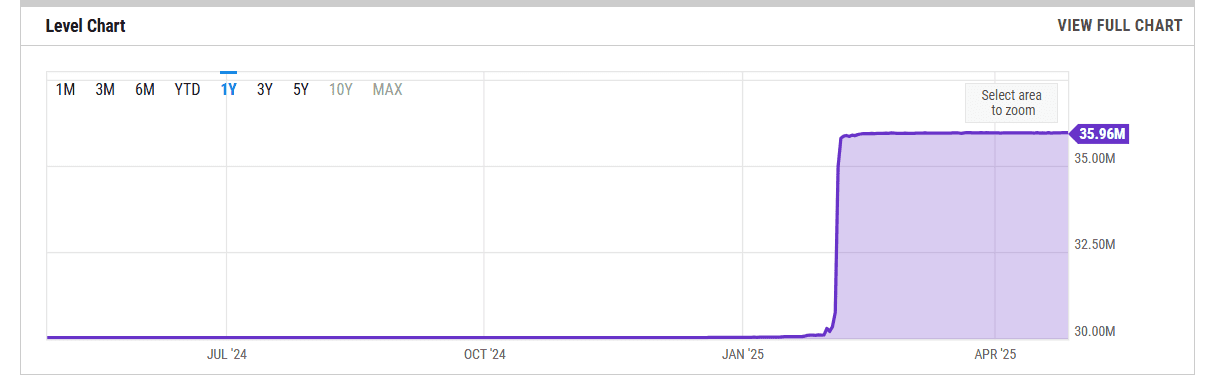
The Ethereum EIP-9698 plan suggests expanding the Ethereum gas limit to 3.6 billion, allowing around 6,000 transactions per block. This expansion would begin from epoch 369017, expected around June 1, 2025.
How the Ethereum Gas Limit Expansion Works in EIP-9698
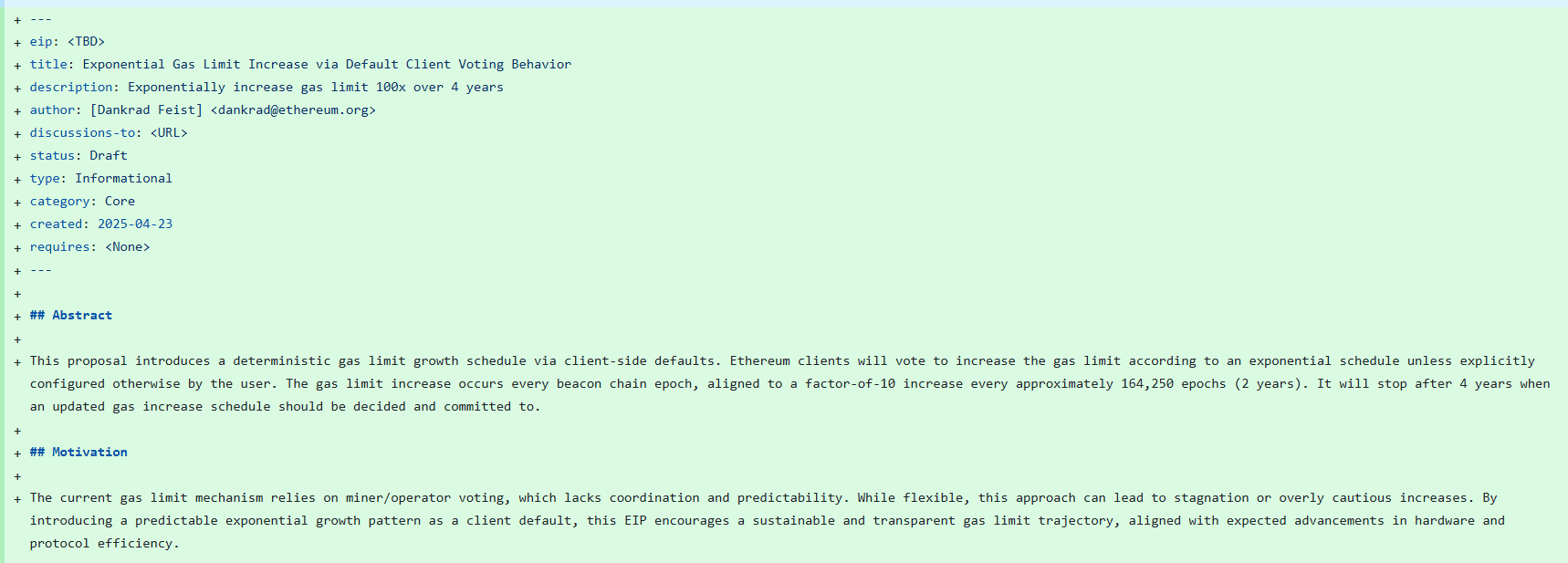
Ethereum EIP-9698 introduces a deterministic gas limit growth model, where Ethereum clients would automatically vote to increase the gas limit unless manually adjusted. This model sets a schedule for exponential gas limit increases at every beacon chain epoch.
The gas limit would grow by a factor of 10 approximately every 164,250 epochs, which equals around two years. Over four years, the model would achieve a 100-fold gas limit expansion, which could bring Ethereum TPS 2000 closer to reality.
Feist stated,
“The current gas limit mechanism relies on miner/operator voting, which lacks coordination and predictability. By introducing a predictable exponential growth pattern as a client default, this EIP encourages a sustainable and transparent gas limit trajectory, aligned with expected advancements in hardware and protocol efficiency.”
This shift would make gas limit adjustments more systematic compared to the current operator-led voting, which Feist noted often results in stagnation or slow changes.
Backward Compatibility and Node Security for Ethereum EIP-9698
Ethereum EIP-9698 is a non-consensus change and maintains full backward compatibility. Nodes that do not adopt the new default behavior will continue operating normally. Clients can still manually adjust settings if preferred.
Feist addressed concerns about network security, highlighting that sudden gas limit increases could strain less-optimized nodes and slow block propagation. However, the gradual schedule is designed to give developers and operators time to adapt.
He added,
“The exponential schedule with very gradual increments per epoch gives node operators and developers ample time to adapt and optimize.”
This cautious growth pattern under Ethereum gas limit expansion aims to support scaling without exposing the network to unnecessary risks.
Ethereum Pectra Upgrade Set to Complement Throughput Improvements
The discussion around Ethereum EIP-9698 coincides with the upcoming Pectra upgrade, set to go live next week. The Pectra upgrade focuses on enhancing blob throughput, reducing Layer 1 transaction fees, and increasing validator flexibility.
It also improves data storage efficiency, aiming to make Layer 2 scaling solutions more effective. These changes complement efforts like Ethereum EIP-9698, which target higher Ethereum throughput upgrades on the mainnet.
At the same time, Ethereum developers continue exploring structural improvements, including a separate discussion proposing to replace Ethereum’s EVM with RISC-V architecture for long-term scalability.
